
With a growing organization and a growing count of repositories it will also be a growing need to centrally enforce repository settings, branch protection, team access and more accross the entire GitHub organization.
What is Safe-Settings
Safe-settings is an app to manage policy-as-code and apply repository settings across an organization. The official repository is found on GitHub.
Create GitHub App
In order to create an app registration from a manifest flow, create a html file with a form and include the manifest.
- The action URL in the form must include the name of the GitHub organization where the app should be created
- The hook url will be updated later
- The redirect url can not be localhost, but the FQDN used here is a made up one
<html>
<body>
<form action="https://github.com/organizations/<organizations-name-here>/settings/apps/new" method="post">
register a GitHub App Manifest: <input type="text" name="manifest" id="manifest"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<script>
input = document.getElementById("manifest")
input.value = JSON.stringify({
... manifest should be app.yml content from the safe-settings repo, converted to json
... plus a redirect url
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
full-example/safe-settings-github-app.html
<html>
<body>
<form action="https://github.com/organizations/eskillarsen/settings/apps/new" method="post">
register a GitHub App Manifest: <input type="text" name="manifest" id="manifest"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<script>
input = document.getElementById("manifest")
input.value = JSON.stringify({
"default_events": [
"branch_protection_rule",
"check_run",
"check_suite",
"create",
"custom_property_values",
"member",
"pull_request",
"push",
"repository",
"repository_ruleset",
"team"
],
"default_permissions": {
"repository_custom_properties": "write",
"organization_custom_properties": "admin",
"actions": "read",
"administration": "write",
"checks": "write",
"contents": "write",
"environments": "write",
"issues": "write",
"metadata": "read",
"pull_requests": "write",
"statuses": "write",
"members": "write",
"organization_administration": "write",
"actions_variables": "write"
},
"name": "safe-settings-eula-demo001",
"url": "https://github.com/eskillarsen",
"public": false,
"redirect_url": "http://localhost.eula.no/remove-this",
"hook_attributes": {
"url": "http://change-later.eula.no/",
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
Open the html file and submit the form.
This should redirect you to GitHub. Here you will have another chance to change the name of the GitHub app.
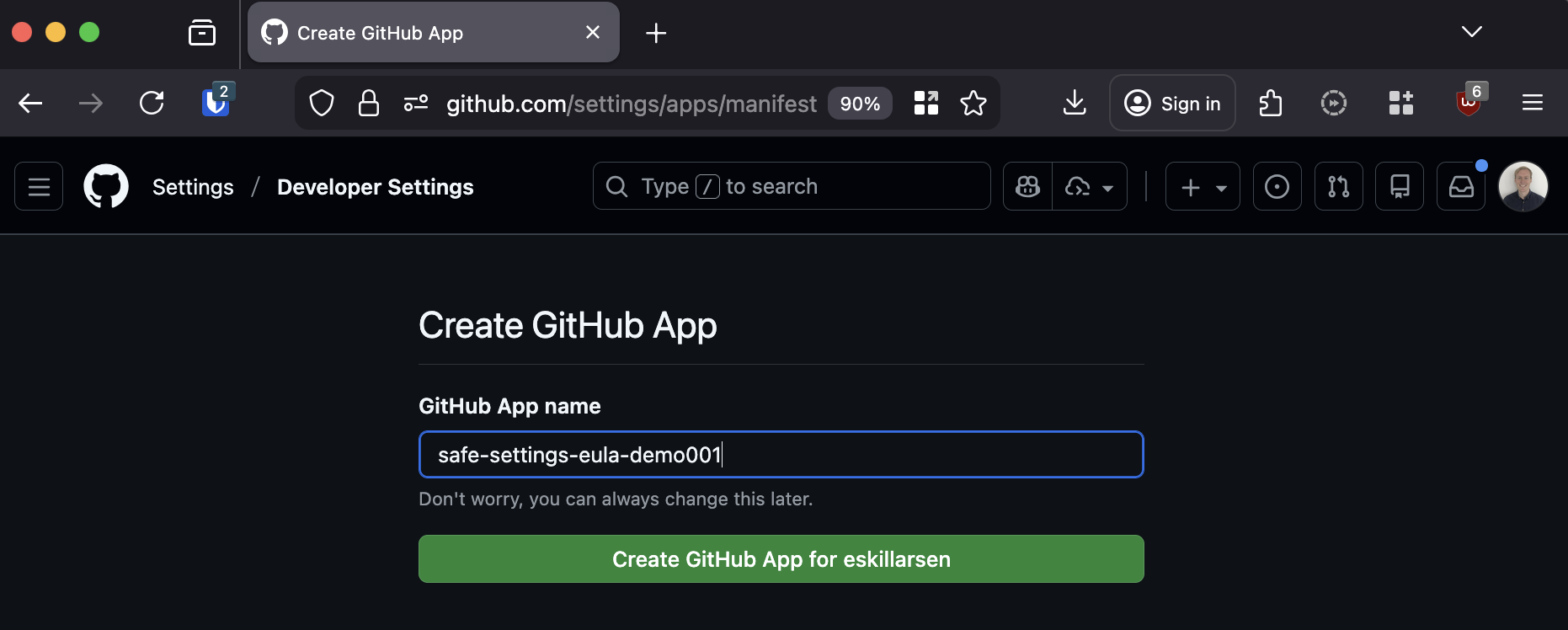
When GitHub has created the app, they redirect to the defined url in the manifest. Included in the redirect url is a code.
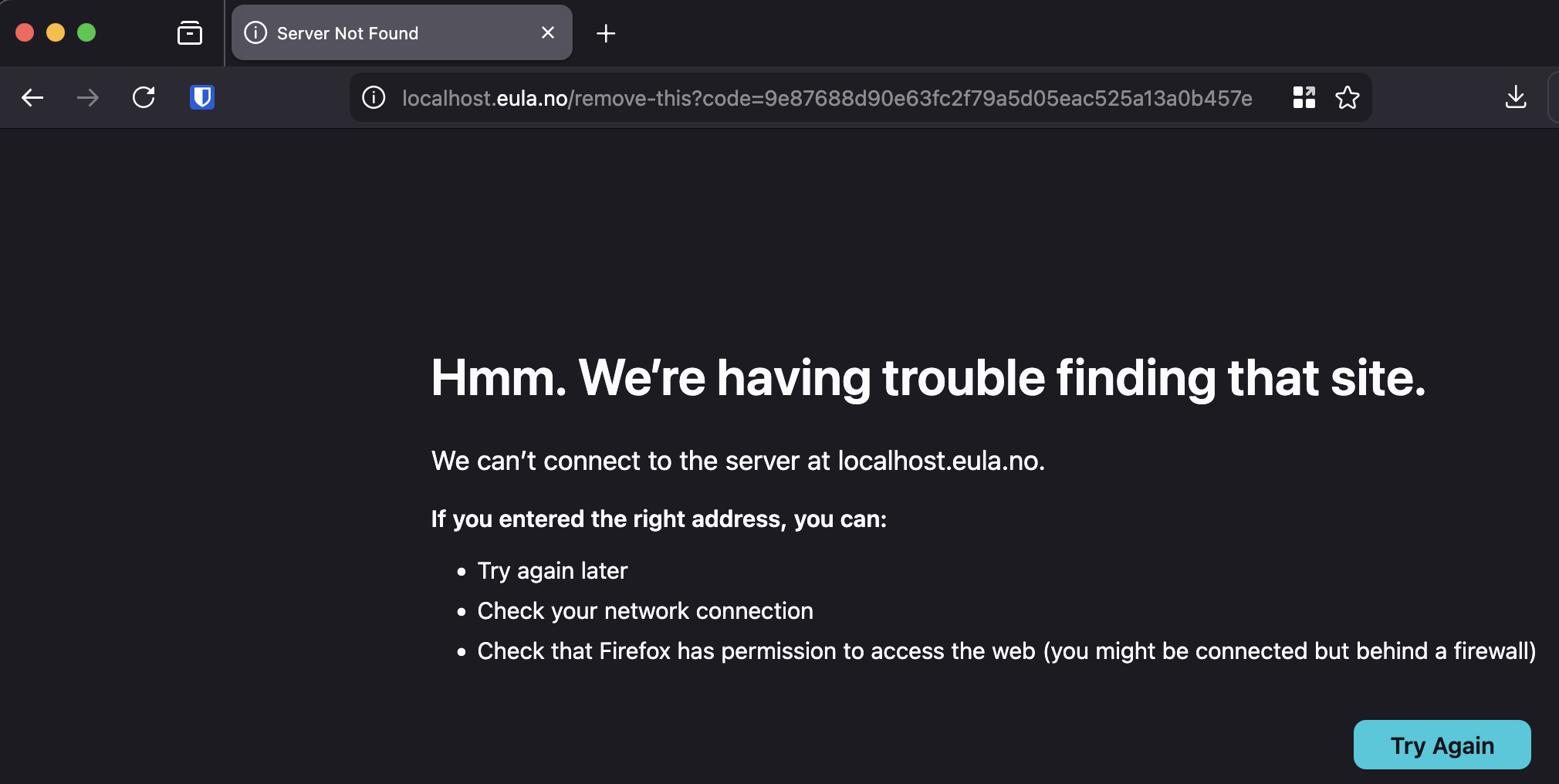
The code will have to be sent to GitHub in another POST request to complete the registration, within one hour.
gh api \
--method POST \
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" \
-H "X-GitHub-Api-Version: 2022-11-28" \
/app-manifests/<code_from_redirect_url>/conversions
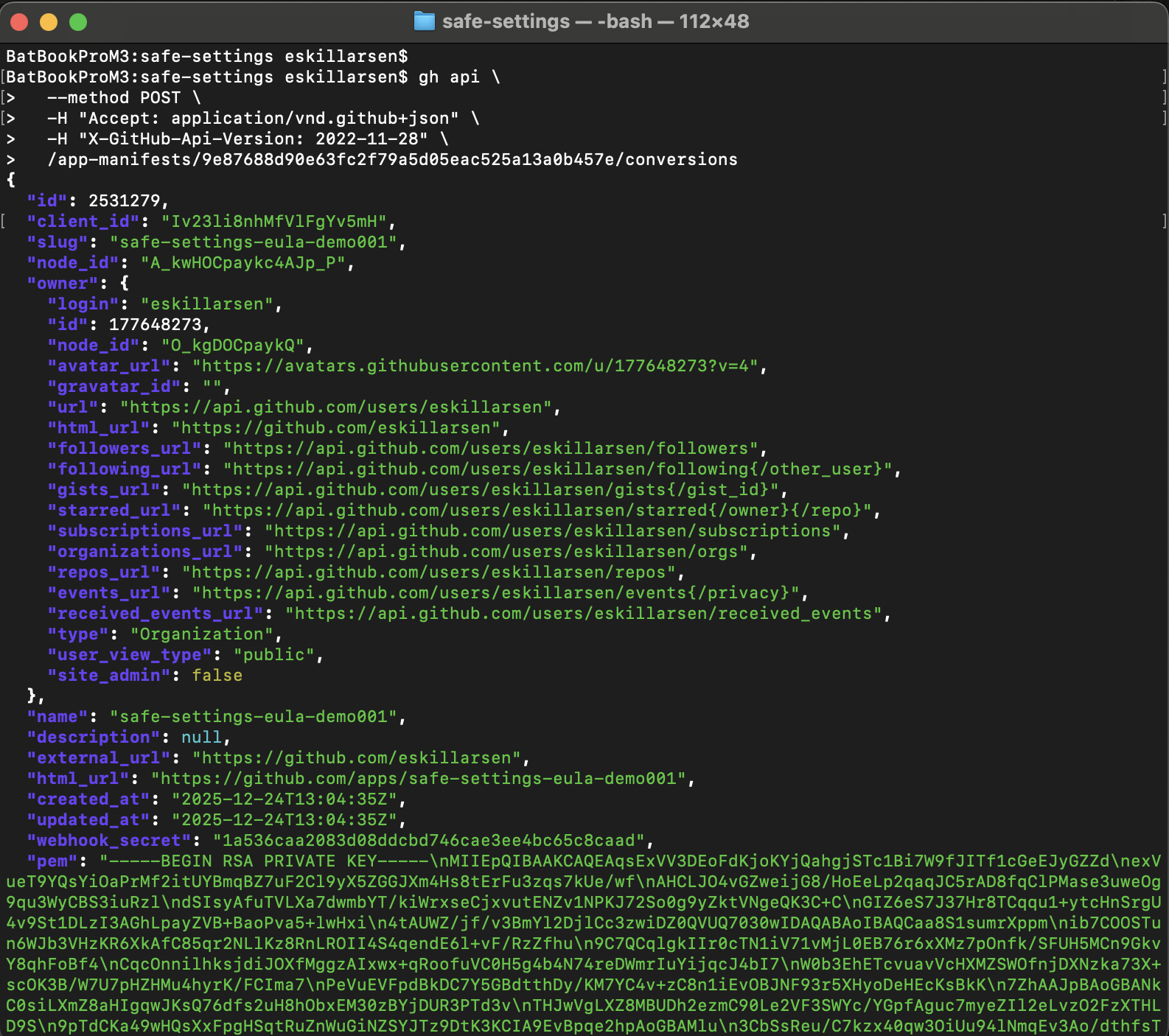
From the response make a note of the app ID, webhook secret and private key.
Run safe-settings
Clone the safe-settings repo and build the image.
git clone https://github.com/github/safe-settings
cd safe-settings
podman build -t safe-settings .
Create the files priv.key and webhooksecret.txt, populate them with the values from the respone during the GitHub App creation. Then run a container with the freshly built image.
Some environment variables is defined in file lib/env.js in the safe-settings repository. Others are found in the ProBot Docs.
podman run \
-e GH_ORG="eskillarsen" \
-e APP_ID="2531279" \
-e PRIVATE_KEY="$(cat priv.key)" \
-e WEBHOOK_SECRET="$(cat webhooksecret.txt)" \
-e LOG_LEVEL="debug" \
-e ADMIN_REPO="safe-settings-demo001" \
-e ENABLE_PR_COMMENT="true" \
-p 3000:3000 \
safe-settings
In order for the container to recieve any webhook traffic from GitHub it needs to be publicly available. Here ngrok is used to expose the local port 3000.
firefox "https://dashboard.ngrok.com/get-started/your-authtoken"
ngrok config add-authtoken abc_XYZ
ngrok http 3000
Ngrok will generate a FQDN, and this FQDN will have to be added to the GitHub App as a webhook URL. This way GitHub can send POST requests to the container when events occur.
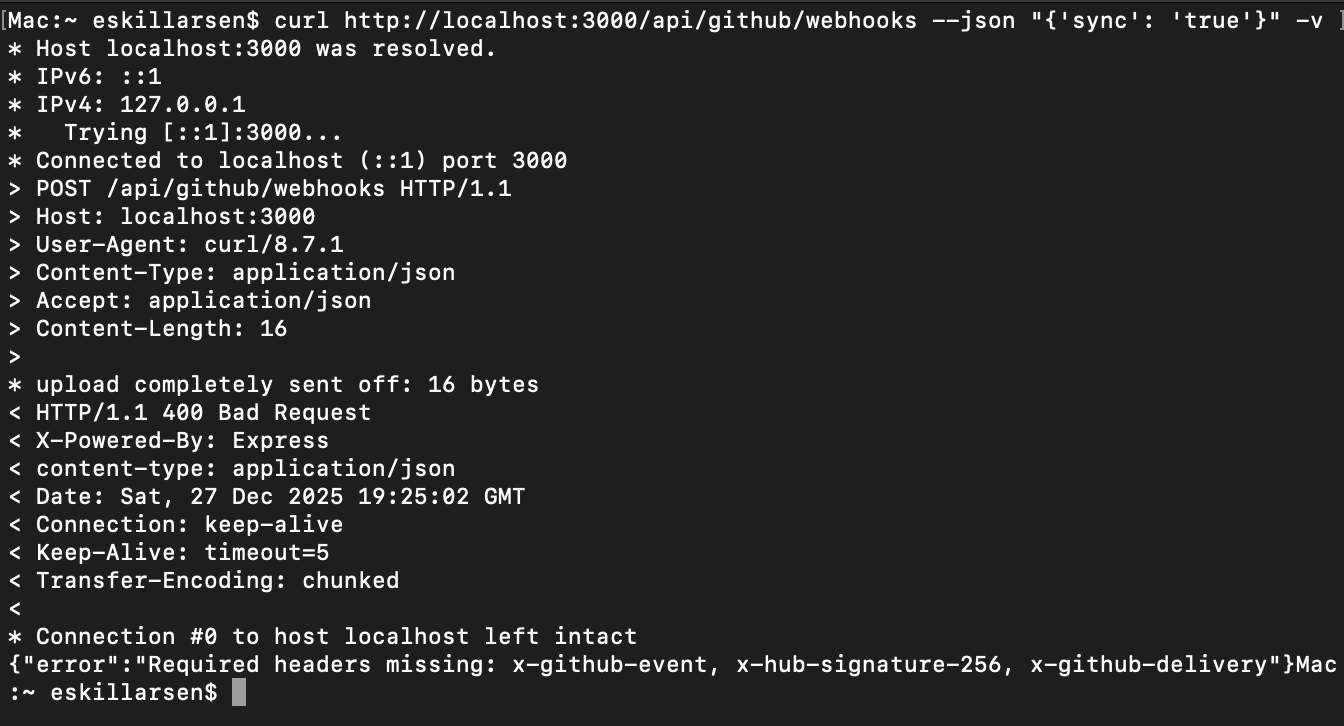
The default webhook path of /api/github/webhooks must be included. It can be changed with the environment variable WEBHOOK_PATH.
Admin repository
Safe-settings will look for a repository named admin by default. In this repository all configuration for the GitHub organization and repositories is stored. To have safe-settings to look for another repository, use the the environment variable ADMIN_REPO.
The structure of the repository should look like this, and some example files is included.
admin/ # Repository name
├── .github/
│ ├── settings.yml # Organization-wide settings
│ ├── suborgs/ # Sub-organization settings
│ │ ├── frontend-team.yml
│ │ └── backend-team.yml
│ └── repos/ # Repository-specific settings
│ ├── demo-repo-1.yml
│ └── demo-repo-2.yml
.github/settings.yml
repository:
description: description of the repo
homepage: https://example.eula.no/
force_create: true
auto_init: true
teams:
- name: example-team
permission: pull
.github/repos/demo-repo-1.yml
repository:
name: demo-repo-1
description: demo-repo-1-description
force_create: true
auto_init: true
gitignore_template: Node
default_branch: master
branches:
- name: default
protection:
required_pull_request_reviews:
required_approving_review_count: 2
dismiss_stale_reviews: true
require_code_owner_reviews: true
require_last_push_approval: true
required_signatures: false
require_linear_history: false
required_status_checks: # null
enforce_admins: false
restrictions: # null
.github/repos/demo-repo-2.yml
repository:
name: demo-repo-2
description: demo-repo-2-description
More complex examples can be found here.
- https://github.com/github/safe-settings/tree/main-enterprise/docs/sample-settings
- https://github.com/ocpdude/safe-settings/tree/main/docs/sample-settings
- https://github.com/UCL-MIRSG/.github/tree/main/safe-settings
Available settings can be found here.
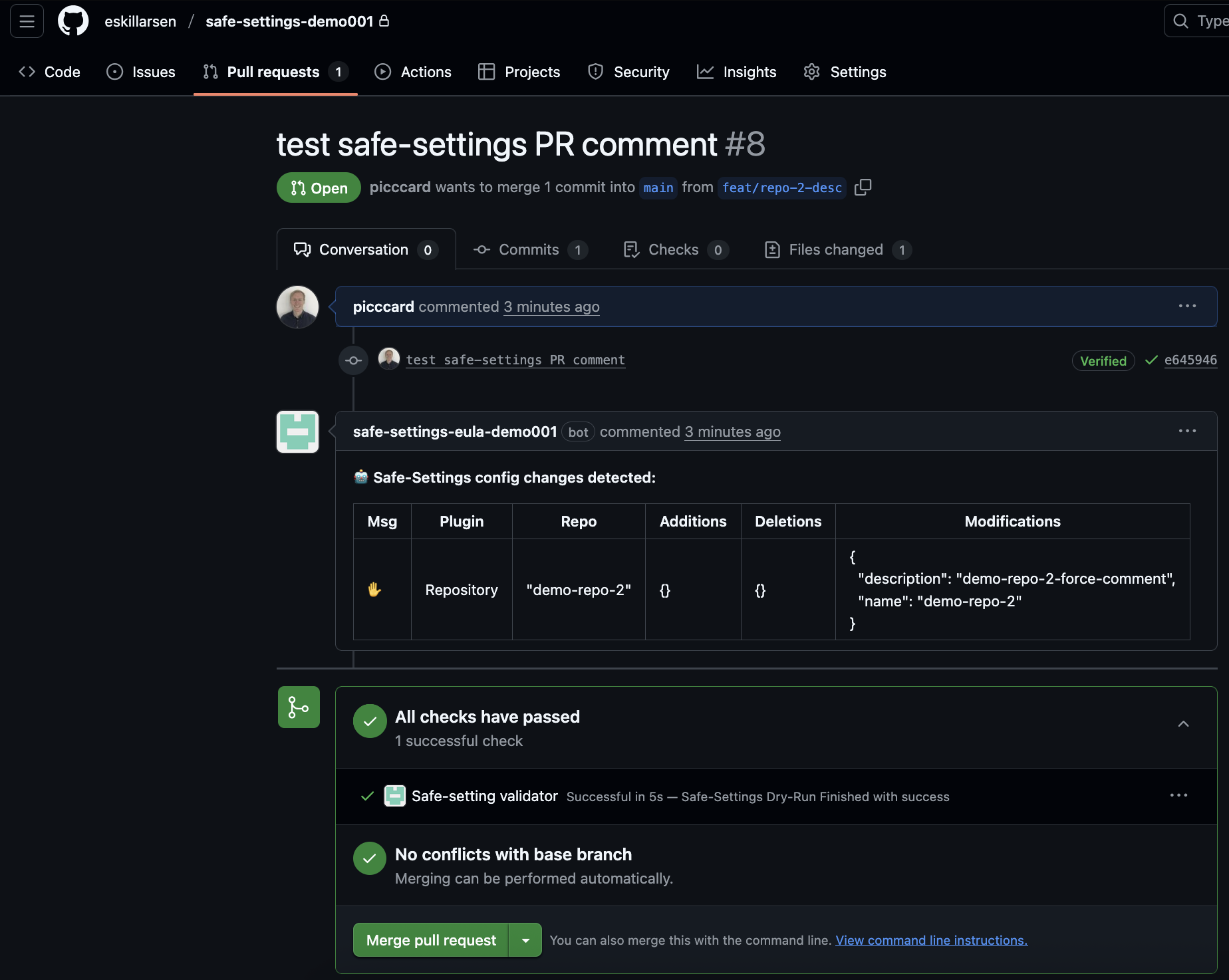
Test Pull Request
When a pull request is added created on the admin repository, the container will recieve the event and plan any modifications. A summary of the modifications will be added as a comment on the PR.
Gotchas
Webhook path
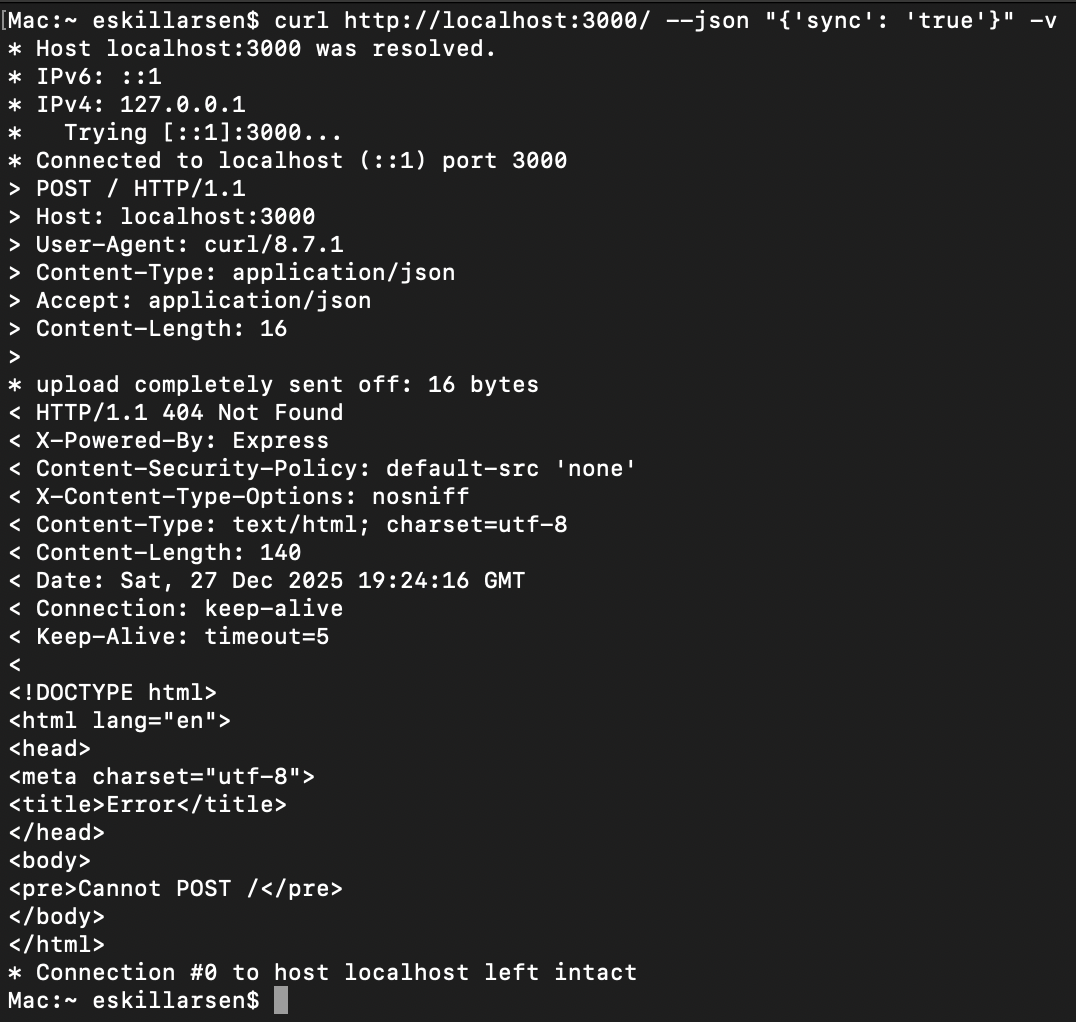
Initially I configured the webhook on the GitHub App to be the root path / and things did not work. When manually sending a POST request to the root path I got a HTTP status of 404 with a message of Cannot POST.
This had to do with a ProBot upgrade as descibed in this issue. The default webhookPath was changed to /api/github/webhooks.
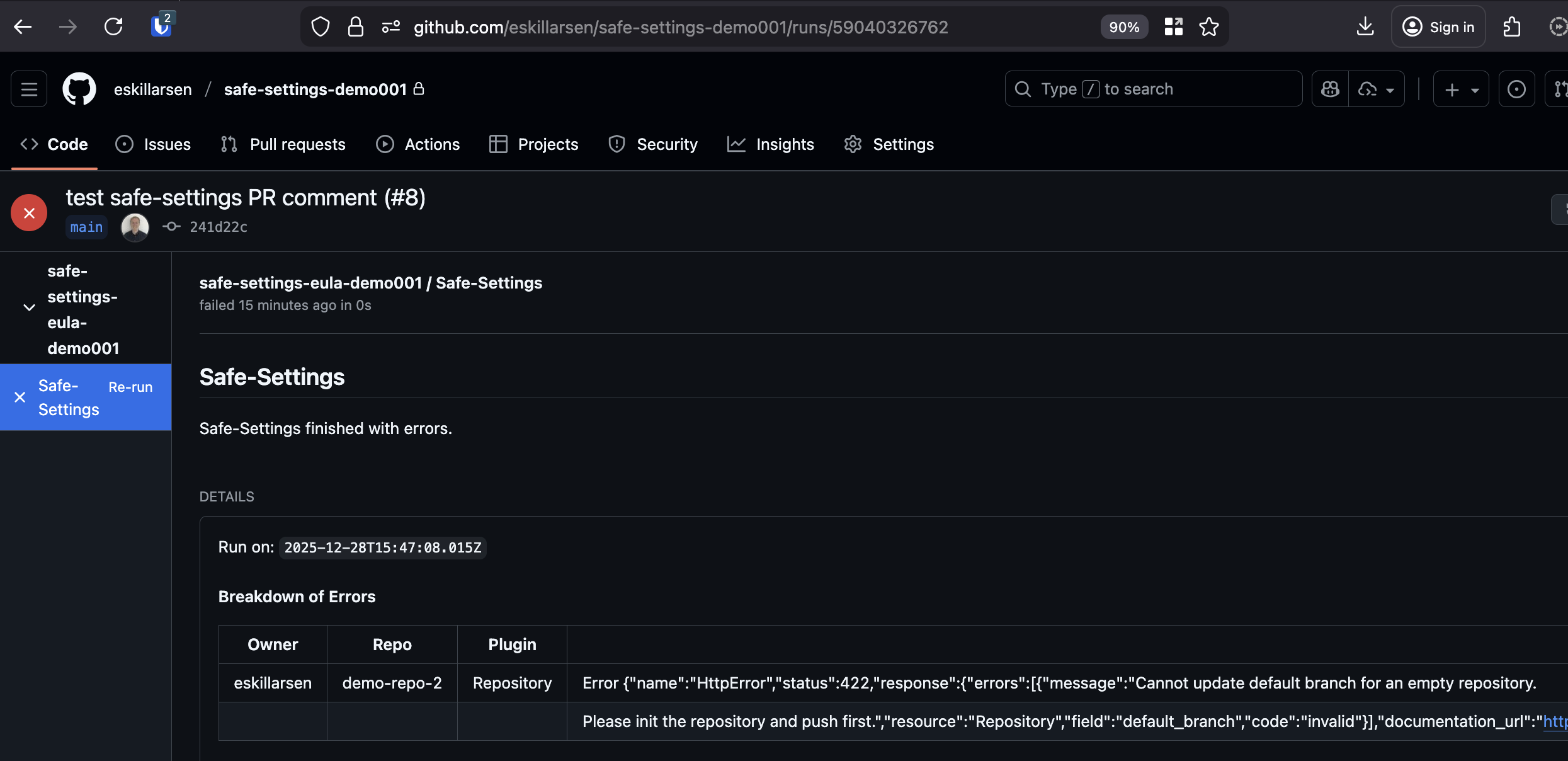
Empty repository
Some settings requires the repo to be initiated, this can cause runs to fail.
Null values
Some required properties can be disabled by setting the value to null. But setting null in the yaml will fail, the correct way is to set it to an empty value.
branches:
- name: default
protection:
required_status_checks: # null
enforce_admins: false
restrictions: # null
required_pull_request_reviews:
required_approving_review_count: 2
required_signatures: false
require_linear_history: false
Deployment config
To control what repositories safe-settings controls, create a file deployment-settings.yml. Use this file to include and/or exclude repositories.
# Using include/exclude
restrictedRepos:
include:
- api
- core-*
exclude:
- admin
- .github
- safe-settings
- test-*
# Or using simple array syntax for includes
restrictedRepos:
- admin
- .github
# ...
This file is loaded when safe-settings starts. When running safe-settings from a container the file must be mounted to the default path of /opt/safe-settings/deployment-settings.yml. Use the environment variable DEPLOYMENT_CONFIG_FILE_PATH if the file is mounted to a custom path.
podman run \
...
-e ADMIN_REPO="safe-settings-demo001" \
-p 3000:3000 \
-v "$(pwd)/deployment-settings.yml":/opt/safe-settings/deployment-settings.yml:ro \
safe-settings
When the webhook recieves an event the logs will look something like this.
{"level":20,"time":123, ...,"msg":"deduped repos []"}
{"level":20,"time":123, ...,"msg":"deduped subOrgs []"}
{"level":20,"time":123, ...,"msg":"deploymentConfig is {\"restrictedRepos\":{\"exclude\":[\"admin\",\".github\",\"safe-settings\",\"admin-*\",\"excl-*\"]}}"}